
Experiential Design for Online Courses
In a recent study, my research group at Harding University explored how a person’s learning context and personal experiences contribute to learning in an online course (Westbrook, McGaughy, and McDonald, 2018). The analysis highlighted the importance of experience as a resource for learning.
In his book Nothing Never Happens, John D. Hendrix (2004) provides a “Sunday School” teaching model that draws from experiential learning theory (see 18-19). Hendrix’s model resembles Kolb’s theory: both focus on the inward active mind of the student and the outward active behavior that leads to learning (see Kolb, 1984, 40-60). Hendrix divides the experiential learning process into four domains and uses terminology that will be easily understood in a ministry context.
When I was first introduced to experiential learning theory, as well as to Hendrix’s model, I was a seminary student who was in the beginning stages of learning how to develop online courses for Harding. At that time, it seemed to me that this cycle of experience, exegesis (or course content), reflection, and application would nicely fit an online, asynchronous learning design. Now, 12 years later, this model has yielded not only successful student learning outcomes time and again, but also students who have expressed appreciation for how much they “related to” and “got something out of” their courses. In the paragraphs below, I’ll share how the model works online.
Experience
The experience of the learner can be something that happened in the past or something that is happening in the present in the student’s world. Everyone brings some kind of experience to learning spaces, and it’s the job of the course designer and facilitator to help the student tap into these experiences for educational purposes. In Hendrix’s words, experiences provide the “hook” onto which new learning materials may hang.
When designing your online course, consider how you might activate the connection between your students and the course content. Encourage students to consider past activities that relate in some way to the learning outcomes of the course. Ask them to share something about their backgrounds. Allow them to share why they want to take your course. Write your discussion questions in such a way that requires them to dip into their own worlds and share them with the rest of the class. Furthermore, create assignments that create new experiences, such as local field trips, conversations with friends and family, interviews with colleagues, or some other type of assignment that opens students’ eyes to the valuable lessons surrounding them.
Exegesis (Content)
Exegesis is the “stuff” of the course. While the word “exegesis” suits Hendrix’s model for a class that centered on a biblical text, I prefer to use “content” in relation to general online course design.
Educators should rest assured that no course content will be harmed or minimized in the creation of an online course. In fact, online courses, especially asynchronous ones often have more pages to read and more videos to watch than traditional classes due to the desire to replace classroom time with reading and viewing time. Providing the appropriate quality and quantity of content is important, but the job doesn’t end here. An experiential online course does more than transmit data to students’ computers.
Reflection
I like to define reflection as the process through which a student internalizes the course content. Another way to say this might be that it is how a student applies the principles and lessons of the content to one’s life.
There are multiple forms of activities that encourage student reflection, such as journaling, concept maps, and personal essays. Any activity that helps students relate personally to what they are learning meet this goal of reflection, especially if the activity encourages metacognition, or thinking about their own thinking. Because of my commitment to social learning, I find great value in discussion boards that prompt personal reflection.
Application
In contrast to reflection, the application space encourages students to apply what they are learning outside themselves. In short, they are to apply the principles and lessons of the course to their real-world context.
As with reflection, I prefer to create prompts in a discussion board that help students see the relevancy of the course to the world beyond the course. This may come in the form of a case study, a hot topic question, or some principle that has broad implications. A summative assignment in which students create real-world solutions with course principles is a great way to help students connect theory with praxis.
Experiential Online Learning Model
When brought together, these four learning domains create an enriching learning experience.
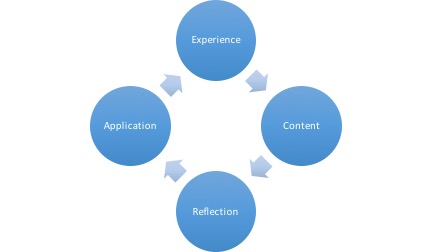
Students at a distance become personally invested in their learning because they have made a personal connection with it. They demonstrate that they have learned content because they are asked to analyze, synthesize, and sometimes create something new with what they have learned. When they reflect on course principles, they internalize what they are learning and discover personal relevancy. By applying what they learn to their contexts, students learn to value the real-world relevancy of their course. This basic four-part model transforms flat, digital correspondence courses into a dynamic, life-developing, learning environment.
Leave a Reply